
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
The fiber is first used in the transmission of light and is suitable for transmitting information over long distances. It is the cornerstone of optical communication in modern information society. The characteristic parameters of light waves propagating in the fiber will change indirectly or directly due to external factors, so that the fiber sensor can analyze and detect changes in these physical quantities, chemical quantities and biomass.
Fiber Optic Sensor
The fiber optic sensor consists of a light source, an incident fiber, an exit fiber, a light modulator, a photodetector, and a demodulator. The basic principle is that the light of the light source is sent to the modulation area through the incident optical fiber, and the light interacts with the measured parameters of the outside in the modulation area, so that the optical properties of the light (such as intensity, wavelength, frequency, phase, partial normal state, etc.) occur. The modulated signal light is changed, and then sent to the photodetector and the demodulator through the exiting optical fiber to obtain the measured parameter.

Fiber optic sensors can be divided into two categories according to the type of structure: one is a functional (sensing type) sensor; the other is a non-functional (light transmitting type) sensor.
Functional sensor
An optical fiber (or a special optical fiber) having sensitivity and detection capability to external information is used as a sensing element to modulate light transmitted in the optical fiber to change characteristics such as intensity, phase, frequency, or polarization state of the transmitted light. The signal to be measured is obtained by demodulating the modulated signal.

The optical fiber is not only a light guiding medium but also a sensitive component, and a multimode optical fiber is often used.
Advantages: compact structure and high sensitivity. Disadvantages: Special fiber is required and the cost is high. Typical examples: fiber optic gyroscopes, fiber optic hydrophones, etc.
Non-functional sensor
It is the use of other sensitive components to sense the measured changes. Optical fibers are only used as the transmission medium for information, and single-mode optical fibers are often used. The optical fiber only serves as a light guide, and the illumination is measured and modulated on the fiber-type sensitive component.
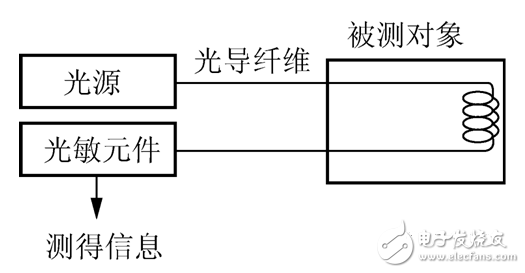
Advantages: no special fiber and other special technologies, easy to implement, low cost. Disadvantages: low sensitivity. Most of the practical applications are non-functional fiber optic sensors.
Depending on the nature of the modulated light wave, both types of fiber sensors can be subdivided into intensity modulated fiber sensors, phase modulated fiber sensors, frequency modulated fiber sensors, polarization modulated fiber sensors, and wavelength modulated fiber sensors.
1) Intensity modulated fiber optic sensor
The basic principle is that the physical quantity to be measured causes a change in the intensity of the transmitted light in the optical fiber, and the measurement to be measured is realized by detecting the change in the light intensity. A constant light source emits light of intensity into the sensing head. In the sensing head, the intensity of the light changes under the action of the signal under test, that is, the external field is modulated, so that the envelope of the output light intensity is The shape of the signal to be measured is the same, and the output current measured by the photodetector is also modulated. The signal processing circuit detects the modulated signal and obtains the measured signal.
The advantages of this kind of sensor are simple structure, low cost and easy implementation. Therefore, it has been developed and applied earlier, and has been successfully applied in displacement, pressure, surface roughness, acceleration, clearance, force, liquid level, vibration, radiation, etc. measuring. There are many ways of intensity modulation, which can be roughly divided into reflective intensity modulation, transmission intensity modulation, optical mode intensity modulation, and refractive index and absorption coefficient intensity modulation.
Generally, the reflection intensity modulation, the transmission intensity modulation, and the refractive index intensity modulation are called external modulation, and the optical mode is called internal modulation. However, due to the limitation of the principle, it is susceptible to fluctuations in the light source and changes in connector loss, so this sensor can only be used in applications where the interference source is small.
2) Phase modulation fiber optic sensor
The basic principle is: under the action of the measured energy field, the phase of the light wave in the fiber changes, and then the interferometric measurement technique is used to convert the phase change into a change in the light intensity, thereby detecting the physical quantity to be tested. The phase modulation type optical fiber sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, large dynamic measurement range, and fast response speed. The disadvantage is that the requirements for the light source are relatively high and the precision of the detection system is relatively high, so the cost is relatively high. .
At present, the main application areas are: acoustic, pressure or vibration sensors using photoelastic effects; current and magnetic field sensors using magnetostrictive effects; electric field and voltage sensors using electrostriction; and rotational angular velocity sensors using Segnack effect (Fiber Optic Gyro) and so on.
3) Frequency modulation fiber optic sensor
The basic principle is to use the Doppler shift effect of the reflected or scattered light of a moving object to detect its moving speed, that is, the optical frequency is related to the motion state between the light receiver and the light source. When they are relatively stationary, the oscillating frequency of the light is received; when there is relative motion between them, the frequency of the received light is frequency-shifted with its oscillating frequency, and the magnitude of the frequency shift is related to the magnitude and direction of the relative motion speed.
Therefore, such sensors are often used to measure the speed of movement of objects. There are other methods for frequency modulation, such as the absorption and fluorescence of some materials with frequency changes with external parameters, and the Brillouin and Raman scattering of quantum interactions is also a frequency modulation phenomenon. Its main application is to measure fluid flow, and other gas sensors that measure the concentration of gas or monitor atmospheric pollution by Raman scattering when the material is exposed to strong light; temperature sensors that use photoluminescence.
4) Polarization modulated optical fiber sensor
The basic principle is to use the change of the polarization state of light to transmit the information of the object under test.
A light wave is a transverse wave whose light vector is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. If the direction of the light vector of the light wave is always the same, but its size changes with the phase, such light is called linearly polarized light. The plane composed of the light vector and the direction of propagation of the light is the vibration plane of the linearly polarized light.
If the size of the light vector remains the same and its direction rotates evenly around the direction of propagation, the trajectory at the end of the light vector is a circle, and such light is called circularly polarized light. If the magnitude and direction of the light vector are regularly changing and the end of the light vector is rotated along an ellipse, such light is referred to as elliptically polarized light.
Polarization-modulated fiber optic sensors can be fabricated using the polarization properties of the light waves. Polarization plays an important role in many fiber optic systems, especially those that include single mode fiber. Many physical effects affect or change the polarization state of light, and some effects can cause birefringence. The so-called birefringence phenomenon is a phenomenon in which a pair of incident light is often decomposed into two refracted lights for a crystal whose optical properties vary with direction. The phase retardation of light through the birefringent medium is a function of the polarization state of the input light.
The polarization state modulation fiber sensor has high detection sensitivity, can avoid the influence of the change of the light source intensity, and the relative phase modulation fiber sensor has a simple structure and convenient adjustment. Its main application areas are: current and magnetic field sensors using Faraday effect; electric field and voltage sensors using bubble effect; pressure, vibration or acoustic sensors using photoelastic effect; temperature, pressure and vibration sensors using birefringence. At present, the most important thing is to monitor high current.
5) Wavelength modulation type optical fiber sensor
The conventional wavelength modulation type optical fiber sensor is realized by utilizing the property that the spectral characteristics of the sensing probe vary with external physical quantities.
Most of these sensors are non-functional sensors. In a wavelength-modulated fiber optic probe, the fiber is simply used as a light guide, that is, the incident light is sent to the measurement area, and the returned modulated light is sent to the analyzer. The key to fiber-optic wavelength detection technology is the good performance of the light source and spectrum analyzer, which has a decisive influence on the stability and resolution of the sensing system.
Optical fiber wavelength modulation technology is mainly used in medicine, chemistry and other fields. For example, analysis of human blood gas, PH value detection, chemical analysis of indicator solution concentration, phosphorescence and fluorescence phenomenon analysis, black body radiation analysis, and Fabry-Perot filter. The so-called wavelength modulation type fiber sensor is mainly referred to as a fiber Bragg grating sensor (FBG).
December 29, 2023
December 28, 2023
October 14, 2022
البريد الإلكتروني لهذا المورد
December 29, 2023
December 28, 2023
October 14, 2022

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.